electron withdrawing groups list|Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups : Clark An electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effects. Electron-withdrawing groups have significant impacts on fundamental chemical processes such as acid-base reactions, redox potentials, and substitution reactions. 3 talking about this
PH0 · Ortho
PH1 · Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups
PH2 · Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry
PH3 · Identifying Electron
PH4 · Electrophilic aromatic directing groups
PH5 · Electron
PH6 · Ch12 : Substituent Effects
PH7 · Activating and Deactivating Groups In Electrophilic Aromatic
PH8 · 6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups
PH9 · 18.6: Substituent Effects on the EAS Reaction
PH10 · 14: Substituent Effects
Lernen Sie mit der Zufalls-Video-Chat von Camgo's sofort neue Leute kennen. Sprechen Sie mit Fremden oder schließen Sie neue Freundschaften.
electron withdrawing groups list*******Activating groups increase the rate; Deactivating groups decrease the rate; EDG = electron donating group; EDG can be recognised by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the π system, eg: -OCH 3; except-R, -Ar or -vinyl (hyperconjugation, π electrons) EWG = .Substituent Effects(contd.) . There are two main electronic effects that substituents .An electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms. This electron density transfer is often achieved by resonance or inductive effects. Electron-withdrawing groups have significant impacts on fundamental chemical processes such as acid-base reactions, redox potentials, and substitution reactions. Electron withdrawing (highly electronegative) nature outweighs donation of electron density through a lone pair. Atoms with pi-bonds to electronegative groups .
Examples of electron donating groups in the relative order from the most activating group to the least activating: -NH 2, -NR 2 > -OH, -OR> -NHCOR> -CH 3 and other alkyl groups with R as alkyl groups (C n H . 1. ortho-, para- Directors. Here’s a fascinating observation. Start with a monosubstituted benzene. Then perform some kind of . Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups. Expand/collapse global location. Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups. Page ID. A substituent on a benzene ring can effect the placement of additional substituents on that .The conjugate bases of many Brønsted superacids have electron-withdrawing substituents that make them such poor Lewis bases that they are useful as .
Substituent groups can be electron withdrawing or electron donating. Electron Withdrawing Groups. Because F pulls electrons toward itself, and positively polarizes .Learn how to identify electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) that enhance the electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon in substitution reactions. See example .Electron withdrawing group (EWG): An atom or group that draws electron density from neighboring atoms towards itself, usually by resonance or inductive effects. Trifluoro acetate ion is a weaker base .
Here are some general pointers for recognising the substituent effects: The H atom is the standard and is regarded as having no effect. Activating groups increase the rate. Deactivating groups decrease the rate. EDG .electron withdrawing groups list Deactivating groups decrease the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution, relative to hydrogen. If you look through the list of ortho- , para- directors, you might recognize that many of them are also .
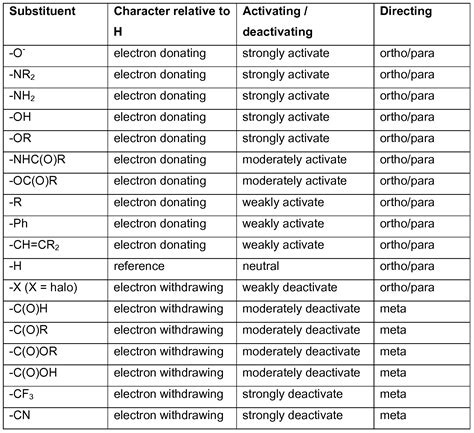
Electron withdrawing groups (EWG) have very much affinity towards electrons. When such a group is present in a molecule then most of the charge density will be partially shifted towards EWG. Eg. In nitromethane , EWG present is present and it is Nitro group(NO2) . In this molecule NO2 has partial negative charge since it attracts the .14: Substituent Effects - UC Santa BarbaraIllustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry. Electron withdrawing group (EWG): An atom or group that draws electron density from neighboring atoms towards itself, usually by resonance or inductive effects. Trifluoro acetate ion is a weaker base than acetate ion because the trifluoromethyl group is attracting electron density away from the .Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups Figure 14.27. For example, the general group Y=Z is an O=N bond in NO2, the O=C bond in R(C=O) and CO2H, the N≡C bond of the CN group, and a C=C bond in aryl groups. We show specific resonance structures for these substituents in section 14.4 that deals with Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution reactions.
Electron with-drawing groups can decrease the electron density at the nucleus, deshielding the nucleus and result in a larger chemical shift. . The effects are cumulative so the presence of more electron withdrawing groups will produce a greater deshielding and therefore a larger chemical shift, i.e. Compound: CH 4: CH 3 Cl: CH 2 Cl 2: CHCl 3 .
The reactivity of aromatic pi bonds in S E Ar reactions is very sensitive to the presence of electron-donating groups (EDG) and electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) on the aromatic ring. This is due to the carbocation nature of the intermediate, which is stabilized by electron-donating groups and destabilized by electron-withdrawing groups.
eg. 1: Thus, the methyl group is an ortho, para directing group. eg. 2: Thus, the nitro group is a meta directing group. Ortho, para directing groups are electron-donating groups; meta directing groups are electron-withdrawing groups. The halide ions, which are electron-withdrawing but ortho, para directing, are the exception.6.4.2: All other things being equal, electron withdrawing groups tend to make Lewis acids stronger and bases weaker while electron donating groups tend to make Lewis bases stronger and acids weaker is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Stephen M. Contakes. The presence of an electron-withdrawing group - such as a fluorine atom - will significantly destabilize a carbocation through the inductive effect. Carbonyl groups are electron-withdrawing by inductive effects, due to the polarity of the \(C=O\) double bond. It is possible to demonstrate in the laboratory (we'll see how in problem 14.x) that .
Substituent groups can be electron withdrawing or electron donating. Electron Withdrawing Groups. Because F pulls electrons toward itself, and positively polarizes the C to which it is bonded, it is called an inductive electron withdrawing group (EWG). The other halogen atoms, as well as the NO2 group (Table 14.02), are also inductive EWGs .Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry. Electron withdrawing group (EWG): An atom or group that draws electron density from neighboring atoms towards itself, usually by resonance or inductive effects. Trifluoro .
Organic Chemistry With a Biological Emphasis by Tim Soderberg (University of Minnesota, Morris) 12.5: Functional Groups and Chemical Shifts in ¹H NMR Spectroscopy is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. An approximate idea of the chemical shifts of the most common types of .Electron withdrawing groups through resonance effect: -NO 2 , Carbonyl group (C=O), -C≡N, -COOH, -SO 3 H etc. Electron donating groups through resonance effect:Just as electron-donating groups can stabilize a carbocation, electron-withdrawing groups act to destabilize carbocations. Carbonyl groups are electron-withdrawing by inductive effects, due to the polarity of the C=O double bond. It is possible to demonstrate in the laboratory that carbocation A below is more stable than carbocation B, even .Here are some general pointers for recognising the substituent effects: The H atom is the standard and is regarded as having no effect. Activating groups increase the rate. Deactivating groups decrease the rate. EDG = electron donating group. EDG can be recognised by lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the π system, eg: -OCH 3. In Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution, an electron-poor aromatic ring is attacked by a nucleophile, resulting in a substitution reaction. The reaction proceeds through a negatively charged (carbanion) intermediate. The reaction is accelerated by the presence of electron-withdrawing groups on the aromatic ring.
100-Question LTO CDE Online Exam Reviewer Answer Key. Use this CDE Validation Exam Reviewer Answer Key to check how well you did in the mock exam in preparation for your driver’s license renewal application. Just make sure you answered everything first before you check the answers so it doesn’t defeat the purpose of the review.
electron withdrawing groups list|Inductive Effects of Alkyl Groups